在进行波动率交易时,尤其是通过像 SVXY、VXX 和 VIXY 这类与交易所挂钩的产品(ETPs)来交易,存在一个支撑所有价格走势的核心概念:展期收益(roll yield)。
对于那些想要利用市场波动率来指导投资和交易的人来说,理解 VIX 期货及其与更广泛市场之间的关系至关重要。而展期收益这一概念,恰恰能解释为什么波动率产品有时会出现令人费解的表现,以及它们如何对市场变化作出响应。
如果你目前还不了解什么是波动率,那强烈建议你先阅读 如何从波动率策略中获利:美股 VIX与市场风暴机会 ,带着疑问再回来看这篇深度解析的文章。
什么是 VIX 期货的展期收益?
展期收益(roll yield) 是指数现货价格与期货价格随时间推移而产生的差异。在波动率 ETPs 的语境下,展期收益描述的是 VIX 期货(基于市场对波动率的预期而交易的期货合约)与 VIX 指数本身(反映当下市场波动率)之间的关系。
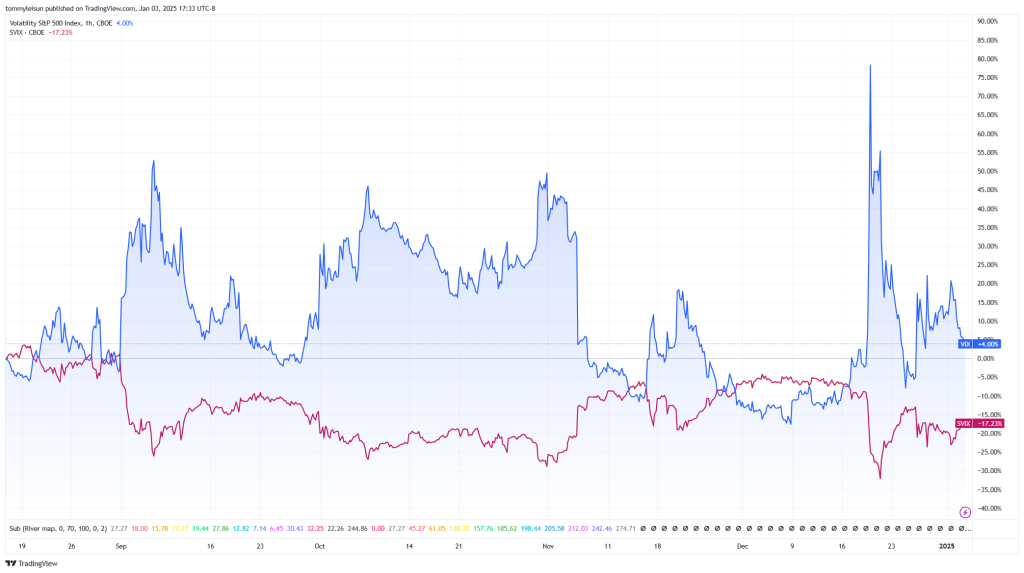
图表 1:VIX 期货期限结构
图示:稳定市场下的 VIX 期货期限结构 | 图片来源:vixcentral.com
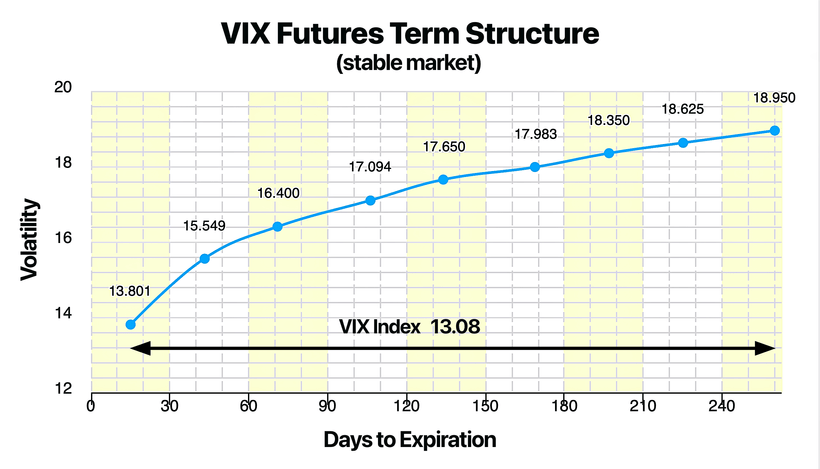
诸如 VXX(做多波动率)和 SVXY(做空波动率)等波动率 ETPs 都基于 VIX 期货,并且只关注最近的两个月期货合约(我称之为 VX1 和 VX2)。这两个合约会被不断地再平衡(rebalanced)并进行配比,从而维持一个30 天常数到期日的合成 VIX 期货,我将其称之为 VXS30。这个 30 天常数到期日合成 VIX 期货的走势至关重要,因为它会直接影响到多头和空头波动率 ETPs 的表现。
举例来说,在做多波动率的产品 VXX 中,如果 VXS30 上涨,那么 VXX 的价格就会上涨;如果 VXS30 下跌,那么 VXX 的价值就会衰减。另一方面,对于反向产品 SVXY 来说,则恰恰相反:当 VXS30 上涨时,SVXY 下跌;当 VXS30 下跌时,SVXY 上涨。
VIX 期货的运作机制
VIX 期货是针对 VIX(基于对标普 500 指数期权的市场波动率测度)未来水平进行投机的合约。它们在市场上不断交易,买卖双方根据各自对未来波动率的预测来决定交易方向。

图表 2:VIX 期货期限结构
图示:在一个稳定市场下,VIX 期货期限结构中展示了月初时的 VXS30(当 VX1 刚开始到期周期)| 图片来源:vixcentral.com
在每个月的 VIX 期货到期周期开始时,VXS30 由 100% 的近月合约(VX1)构成,而第二个月合约(VX2)的比重为 0%。随着月份的推移,为了维持这个“30 天常数到期日”的特性,VXS30 会逐渐卖出部分 VX1 并买入部分 VX2(即第二个月的 VIX 期货)。
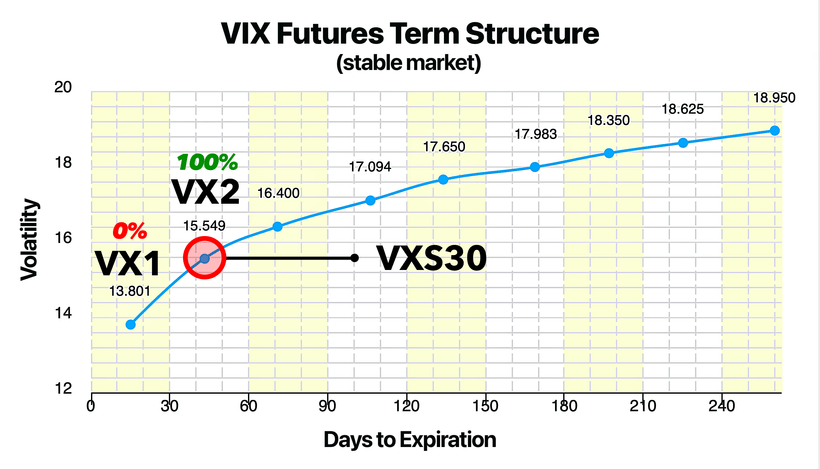
图表 3:VIX 期货期限结构 | VXS30 向 VX2 推进
图示:在一个稳定市场下,VIX 期货期限结构显示当 VXS30 接近到期周期尾声时,它向 VX2 移动的过程 | 图片来源:vixcentral.com
到每个月到期周期结束时,VXS30 会变为 100% 由 VX2 构成,而 VX1 则变为 0%。这种再平衡本身对价格没有直接影响;然而,在这个再平衡过程中所产生的展期收益,却对波动率 ETPs 的定价有着显著影响。

图表 4:VIX 期货期限结构 | VXS30 = VIX(到期时)
图示:VIX 期货期限结构在一个稳定的市场中,VX1 在到期时与 VIX 数值相当 | 图片来源:vixcentral.com
这种过程每个月都会发生:到期日的 VX1 与 VIX 本身数值相等(即同步),VX2 变成新的 VX1,VX3 变成新的 VX2,以此类推,依次推动每个月的 VIX 期货循环往复。
正展期收益与负展期收益
VXS30 与 VIX 指数之间的关系,界定了展期收益。一般而言,有两种情形需要考虑:
- 正展期收益(Positive Roll Yield)
当 VXS30 的交易价格高于 VIX 指数的现货价格时,它在到期日到来之前,很可能会随时间推移而下行,并逐渐向到期时的 VIX 指数靠拢。这种下跌会导致做多波动率 ETP(如 VXX)的价值减少,同时推高做空波动率 ETP(如 SVXY)的价值。 - 负展期收益(Negative Roll Yield)
当 VXS30 的交易价格低于 VIX 指数的现货价格时,情况则相反。VXS30 很可能会随着到期的临近而上涨,并逐渐向 VIX 指数靠拢。在这种情况下,VXX 和 UVXY 这类做多波动率 ETP 受益,它们的价值会随着 VXS30 的上涨而上升;而做空波动率的产品(如 SVXY)则会贬值。
展期收益与市场环境
理解不同市场环境下展期收益的表现,对波动率交易者而言至关重要。在相对稳定的市场环境中,VIX 往往保持在较低水平,VIX 期货一般呈现期货升水(Contango),即期货合约价格高于当前 VIX 指数。这常常表现为期限结构曲线沿着高于 VIX 的位置向上倾斜。
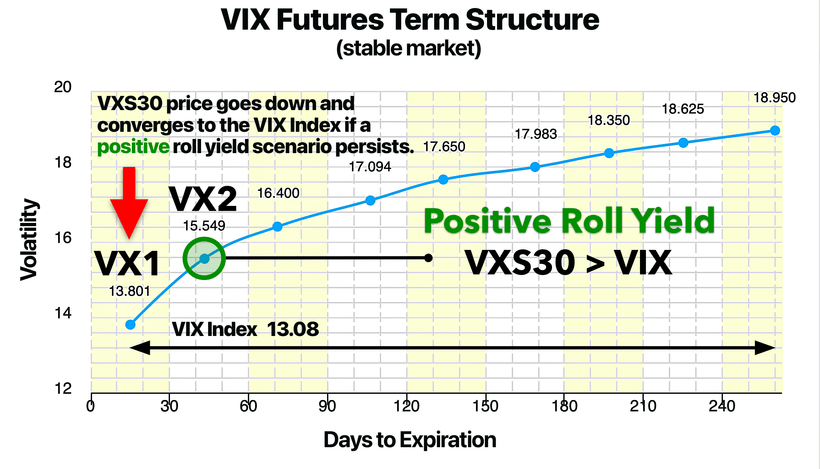
图表 5:VIX 期货期限结构 | 正展期收益
图示:在一个稳定的市场环境中,VXS30 > VIX,表示出现正展期收益 | 图片来源:vixcentral.com
这种情况会产生正展期收益,从而逐步侵蚀做多波动率 ETP 的价值,让它们随着时间推移而贬值。这也解释了为什么 VXX 等产品自推出以来已经下跌超过 99%——正展期收益使其不断衰减。
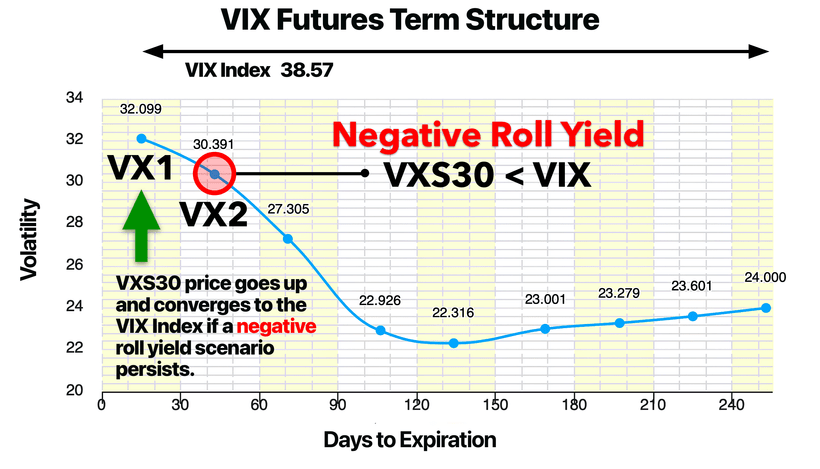
图表 6:VIX 期货期限结构 | 负展期收益
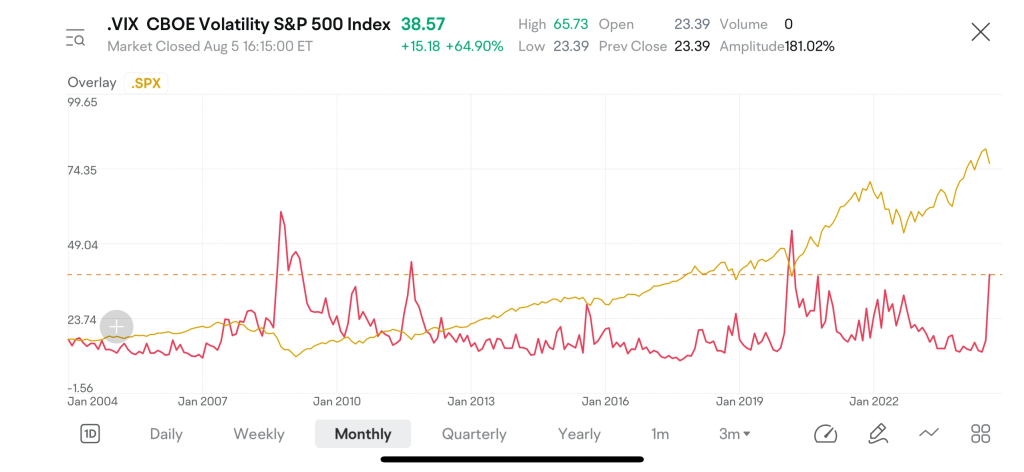
图示:在一个不稳定的市场环境中,VXS30 < VIX,表示出现负展期收益 | 2024年8月5日 | 图片来源:vixcentral.com
另一方面,在波动剧烈或混乱的市场环境中,比如市场崩盘时,VIX 通常会飙升,而 VIX 期货可能进入期货贴水(Backwardation),此时现货 VIX 价格高于期货价格。这种情况下,就会出现负展期收益,推动做多波动率产品(如 VXX 和 VIXY)的价值上涨。
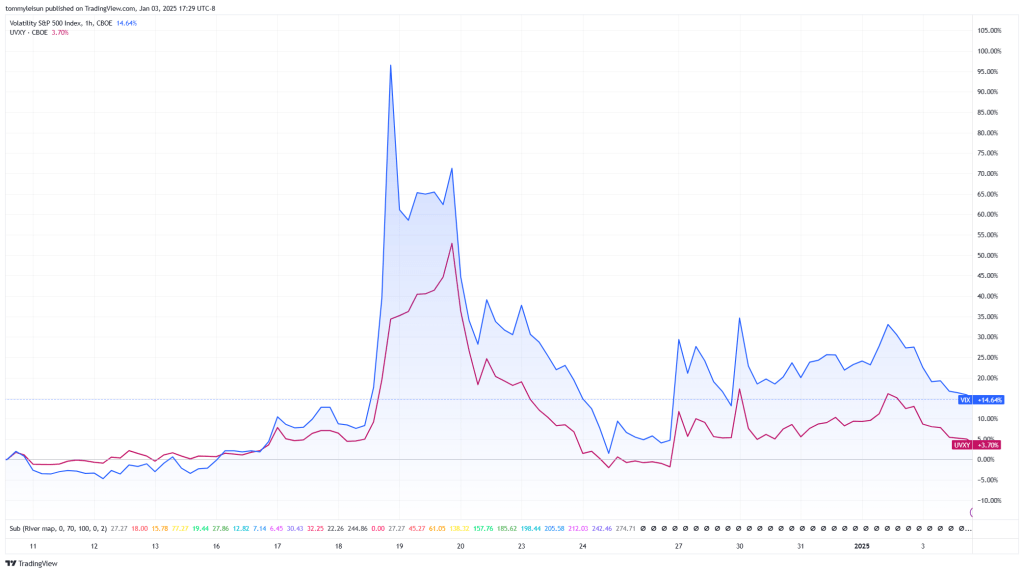
举例来说,在最近一次波动率飙升——2024年8月期间,日本利差交易(carry trade)的崩盘导致 VIX 指数飙升至 65。当时,VXS30 远低于 VIX 指数,形成了负展期收益。随着 VXS30 开始上行,做多波动率的 ETP 也随之飙升。
用一个真实案例,展示了如何抓住难得的行情机遇:2024 年 8 月 2 日(星期五),VIX期货有进入期货贴水的迹象,买入 VXZ(中期做多波动率 ETP);到了 8 月 5 日(星期一),期货贴水逐步减弱马上卖出VXZ,在短短一天内就斩获了 12% 的可观收益。更值得一提的是,如果当时换成买 VIXM,回报率可以达到 22%——这就是如何在小小的市场混乱中收获可观利润的实例!
展期收益对波动率 ETP 的影响
在了解了展期收益的基本概念后,让我们进一步探讨这一现象如何影响特定的波动率产品:
VXX 和 VIXY(做多波动率)
VXX 和 VIXY 持有的是近月和次近月的 VIX 期货多头头寸。当 VIX 期货期限结构发生变化时,这些产品会受到展期收益的影响。在典型的期货升水(正展期收益)环境下,VXX 和 VIXY 的价值会随着 VIX 期货价格向现货 VIX 指数收敛而不断贬值(参见上文图表 5)。
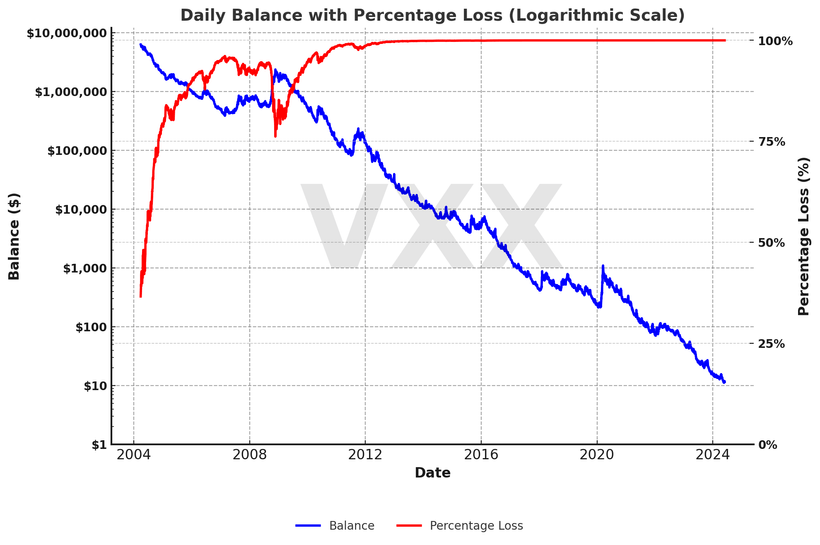
图表 7:VXX 的假设交易场景
对数坐标图:这是对 VXX 进行长期买入并持有(千万不要这么做)的一个假设情况。假设最初投入 1,000 万美元,如今账户余额仅剩不足 12 美元,跌幅高达 99.99%。VXX 于 2009 年推出,上述数据在此之前做了回溯模拟至 2004 年 3 月 26 日。
随着时间的推移,这会导致做多波动率产品遭受重大损失,这也是为什么 VXX 和 VIXY 自诞生以来已经下跌了 99.9% 的原因。
然而,在出现期货贴水(负展期收益)的时期,VXX 和 VIXY 可能获得显著的涨幅。当 VIX 飙升、而 VIX 期货价格滞后时,展期收益由正转负,VXX 和 VIXY 会因为期货价格向高企的 VIX 指数靠拢而受益(参见上文图表 6)。
SVXY(做空波动率)
SVXY 则采取相反的操作方式——它持有近月和次近月 VIX 期货的空头头寸。在正展期收益环境(期货升水)下,VIX 期货价格趋于下行,SVXY 因而受益并上涨。这正是为什么在低波动率、稳定市场中,SVXY 通常能获得较为一致的收益。
但需要注意的是,在负展期收益环境(期货贴水)下,SVXY 面临巨大风险。当 VIX 期货价格上行以接近更高的现货 VIX 指数时,SVXY 就会出现大幅亏损。2018 年 2 月的 “Volmageddon” 事件就是典型案例,SVXY(1 倍杠杆)在一天之内暴跌逾 80%。自那之后,SVXY 的杠杆倍数被降至 0.5 倍,使其在波动率交易中风险相对可控。
展期收益的长期动态
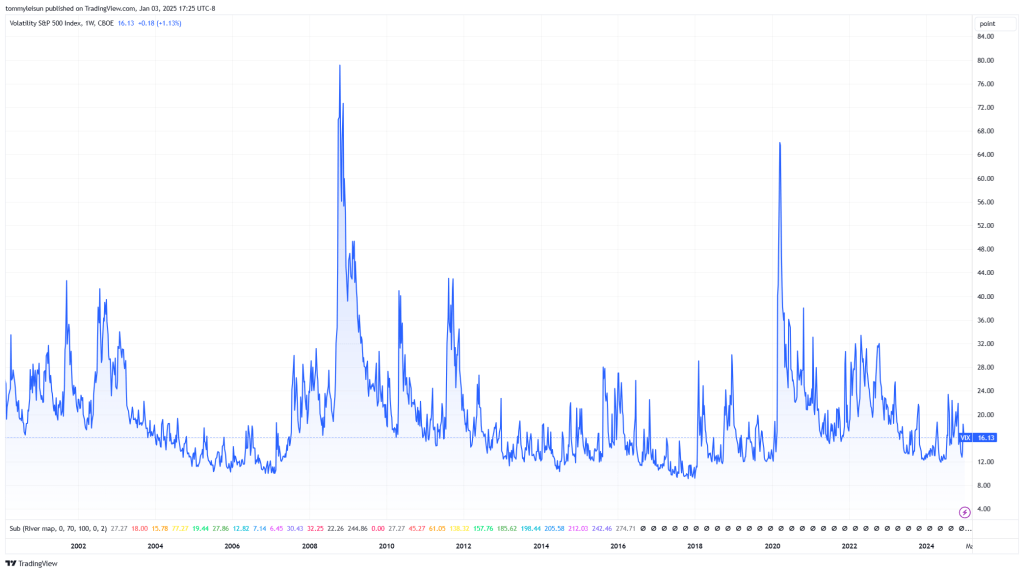
鉴于展期收益的机制及典型市场环境,很容易理解为何做多波动率的产品(如 VXX 和 VIXY)会随着时间推移而不断贬值。自 2004 年 VIX 期货推出以来,VIX 期货期限结构在 80% 以上的时间处于期货升水(正展期收益),这就导致做多波动率 ETP(VXX、VIXY、UVXY 等)长期处于下行趋势,价格不断被展期收益侵蚀。与此相反,做空波动率的产品(如 SVXY)在这段时间里则从持续的升水环境中受益,获得了正面的长期回报。
如何运用展期收益进行交易
了解了展期收益对波动率 ETP 的影响之后,交易者可以将这一认识应用到交易策略中。
1. 交易做多波动率 ETP
如果想利用 VXX 或 VIXY 等产品获取收益,交易者需要密切关注市场环境。由于在稳定市场中正展期收益会让这些产品的价值不断下降,因此最好在高波动或市场不确定性较强时(即负展期收益开始发挥作用时)再考虑介入。
需要强调的是,想要恰到好处地把握此类交易时机极其困难。针对这种情况,个人更偏好使用 VIXM(一个跟踪更远期合约的做多波动率 ETP)。我平均一年中只在不到 3% 的交易日里会用到它。VIXM 相较 VXX 和 VIXY 来说波动更小,因为它关注 VX4 到 VX7 等期限更长的 VIX 期货合约,因此在交易时心理压力也相对更可控。
2. 交易做空波动率 ETP
对于想在稳定市场环境下(即期货升水、正展期收益的常态)获得更稳定回报的交易者而言,SVXY 这样的逆向波动率产品是一个相对更有吸引力的选择。不过,必须警惕在市场崩盘或波动率飙升时期,展期收益会迅速转变为负值,导致 SVXY 的严重亏损。
我采用了一种精密、量化且基于规则的策略来应对这些潜在风险。不管是交易 ETP 还是股票,我都能及时在严重亏损发生前切换到更安全的头寸,保护资金,直到市场波动性下降、恢复稳定。这的确是一套行之有效、可赢利的强大组合策略。
“在混乱中寻得清晰,才能发现机遇所在。”
结论
在波动率交易的世界里,理解 VIX 期货的展期收益 至关重要。它决定了各种波动率 ETP 的价格走势,并解释了像 VXX 这类产品为何会在长期表现上不断贬值。通过关注 VIX 期货期限结构以及 VXS30 与现货 VIX 指数的关系,交易者可以更准确地判断何时应该买入或卖出波动率产品。无论是在混乱市况中交易做多波动率 ETP,还是在稳定市况下交易做空波动率 ETP,展期收益都是驾驭波动率交易世界的重要钥匙。